Individuals suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) often experience a range of digestive symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. While there is no cure for IBS, managing the condition through diet and lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms and overall quality of life.
Understanding IBS and its Triggers
IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine and can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. While the exact cause of IBS is unknown, certain triggers such as stress, hormonal changes, and diet can exacerbate symptoms.
The Role of Diet in IBS
Diet plays a crucial role in managing IBS symptoms as certain foods can trigger flare-ups and worsen digestive issues. It is important for individuals with IBS to identify their personal trigger foods and make appropriate dietary changes to alleviate symptoms.
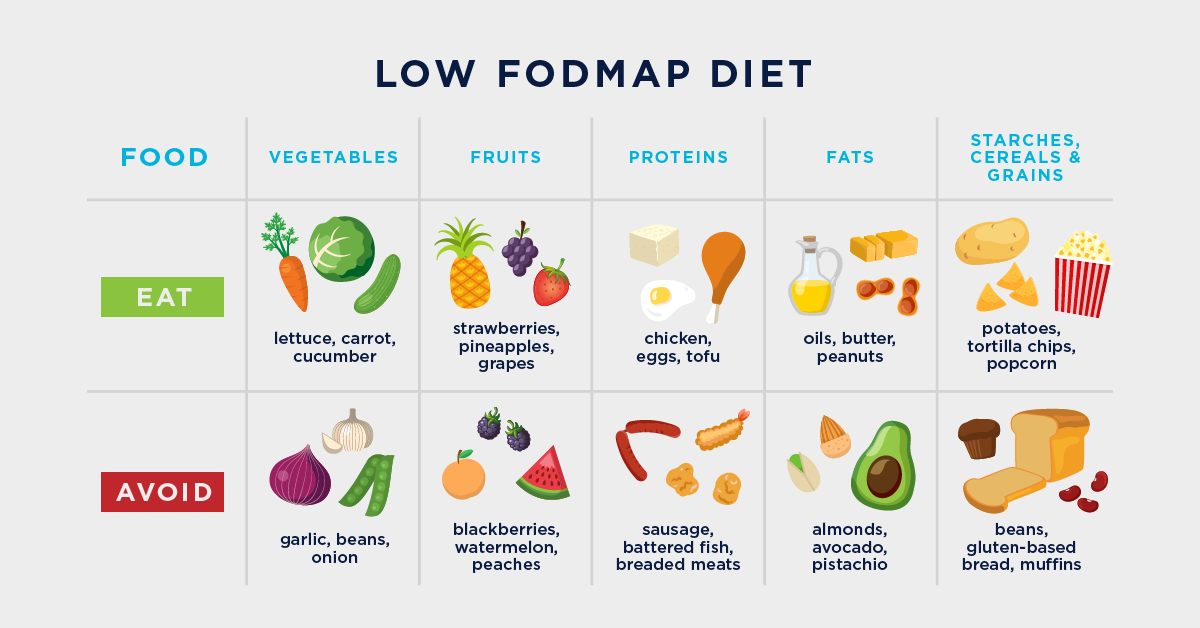
Foods to Avoid
High-FODMAP Foods: Foods high in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) such as onions, garlic, wheat, and certain fruits can trigger symptoms in individuals with IBS.
Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and worsen symptoms of IBS. Limiting or avoiding these beverages can help alleviate discomfort.
Fatty Foods: Foods high in saturated fats can be difficult to digest and may contribute to diarrhea and bloating in individuals with IBS.
Foods to Incorporate
High-Fiber Foods: Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate bowel movements and promote digestive health in individuals with IBS.
Probiotic Foods: Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria and improve symptoms of IBS.
Lean Proteins: Lean proteins like poultry, fish, and tofu are easier to digest and less likely to trigger gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with IBS.
Additional Tips for Managing IBS
In addition to making dietary changes, individuals with IBS can benefit from incorporating the following tips into their daily routine:
Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate symptoms of IBS. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements in individuals with IBS.
Consult a Dietitian: Working with a registered dietitian who specializes in digestive health can help individuals with IBS create a personalized meal plan and identify trigger foods.
Conclusion
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing IBS, incorporating dietary changes and lifestyle modifications can greatly improve symptoms and quality of life for individuals with this condition. By identifying trigger foods, incorporating gut-friendly foods, and implementing stress-reducing techniques, individuals with IBS can effectively manage their symptoms and lead a healthier, more comfortable life.